Reportes Statements, страница 165 - гдз по английскому языку 10 класс (starlight) учебник Баранова, Дули

Авторы: Баранова К. М., Дули Д., Копылова В. В., Мильруд Р. П., Эванс В.
Тип: Student's book (Учебник)
Серия: starlight (звёздный английский)
Издательство: Просвещение, Express Publishing
Год издания: 2019 - 2026
Уровень обучения: углублённый
Цвет обложки: белый, бирюзовый
ISBN: 978-5-09-112205-3
Допущено Министерством просвещения Российской Федерации
Популярные ГДЗ в 10 классе
Grammar Practice Section. Module 2 - страница 165.
Reportes Statements (с. 165)
Условие. Reportes Statements (с. 165)
скриншот условия
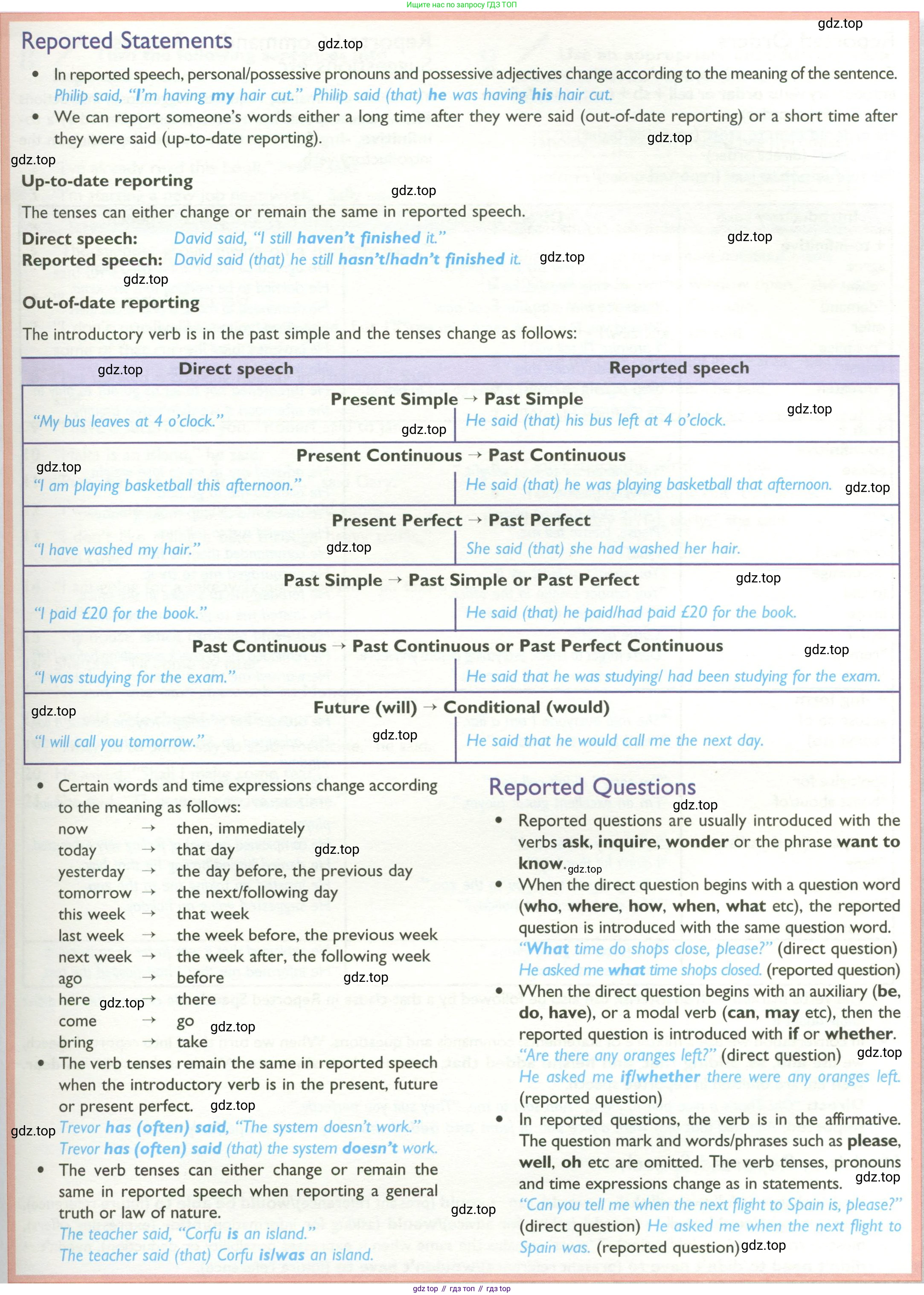
Reported Statements
- In reported speech, personal/possessive pronouns and possessive adjectives change according to the meaning of the sentence. Philip said, "I'm having my hair cut." Philip said (that) he was having his hair cut.
- We can report someone's words either a long time after they were said (out-of-date reporting) or a short time after they were said (up-to-date reporting).
Up-to-date reporting
The tenses can either change or remain the same in reported speech.
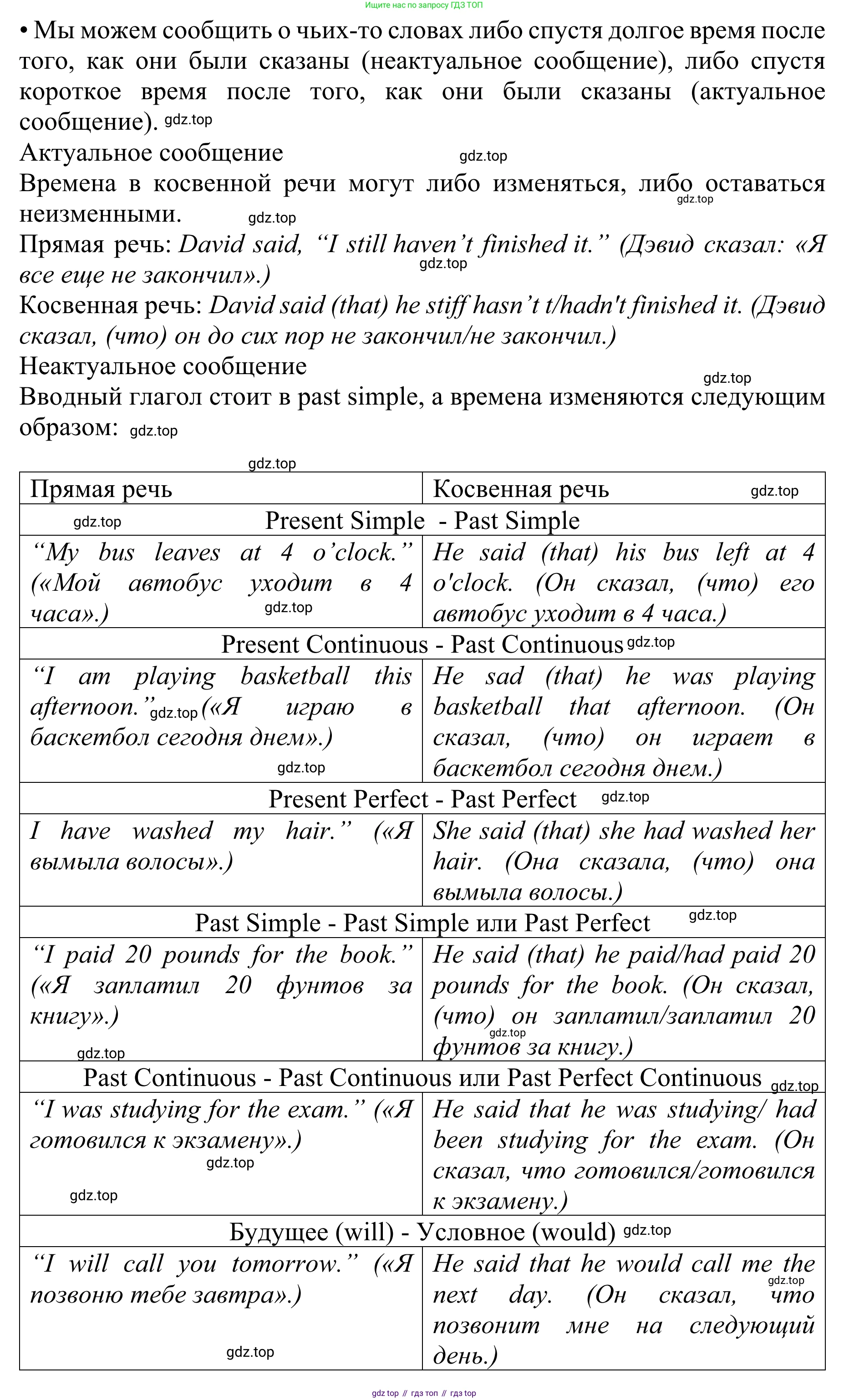
Direct speech: David said, "I still haven't finished it."
Reported speech: David said (that) he still hasn't/hadn't finished it.
Out-of-date reporting
The introductory verb is in the past simple and the tenses change as follows:
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|
| Present Simple → Past Simple | |
| "My bus leaves at 4 o'clock." | He said (that) his bus left at 4 o'clock. |
| Present Continuous → Past Continuous | |
| "I am playing basketball this afternoon." | He said (that) he was playing basketball that afternoon. |
| Present Perfect → Past Perfect | |
| "I have washed my hair." | She said (that) she had washed her hair. |
| Past Simple → Past Simple or Past Perfect | |
| "I paid £20 for the book." | He said (that) he paid/had paid £20 for the book. |
| Past Continuous → Past Continuous or Past Perfect Continuous | |
| "I was studying for the exam." | He said that he was studying/ had been studying for the exam. |
| Future (will) → Conditional (would) | |
| "I will call you tomorrow." | He said that he would call me the next day. |
- Certain words and time expressions change according to the meaning as follows:
- now → then, immediately
- today → that day
- yesterday → the day before, the previous day
- tomorrow → the next/following day
- this week → that week
- last week → the week before, the previous week
- next week → the week after, the following week
- ago → before
- here → there
- come → go
- bring → take
- The verb tenses remain the same in reported speech when the introductory verb is in the present, future or present perfect.
Trevor has (often) said, "The system doesn't work."
Trevor has (often) said (that) the system doesn't work.
- The verb tenses can either change or remain the same in reported speech when reporting a general truth or law of nature.
The teacher said, "Corfu is an island."
The teacher said (that) Corfu is/was an island.
Reported Questions
- Reported questions are usually introduced with the verbs ask, inquire, wonder or the phrase want to know.
- When the direct question begins with a question word (who, where, how, when, what etc), the reported question is introduced with the same question word.
"What time do shops close, please?" (direct question)
He asked me what time shops closed. (reported question)
- When the direct question begins with an auxiliary (be, do, have), or a modal verb (can, may etc), then the reported question is introduced with if or whether.
"Are there any oranges left?" (direct question)
He asked me if/whether there were any oranges left. (reported question)
- In reported questions, the verb is in the affirmative. The question mark and words/phrases such as please, well, oh etc are omitted. The verb tenses, pronouns and time expressions change as in statements.
"Can you tell me when the next flight to Spain is, please?" (direct question)
He asked me when the next flight to Spain was. (reported question)
Решение 1. Reportes Statements (с. 165)



Решение 3. Reportes Statements (с. 165)
Что такое косвенная речь и каковы основные правила её использования, согласно представленному тексту?
Ответ:
1. Tense Changes (Backshift): When the introductory verb is in the past, the verb tenses in reported speech usually move one step back into the past. For example: Present Simple becomes Past Simple, Present Perfect becomes Past Perfect, and Future (will) becomes Conditional (would).
(1. Изменение времен (Backshift): Когда вводный глагол стоит в прошедшем времени, времена глаголов в косвенной речи обычно сдвигаются на один шаг в прошлое. Например: Present Simple становится Past Simple, Present Perfect становится Past Perfect, а Future (will) становится Conditional (would).)
2. Pronoun and Possessive Changes: Personal pronouns and possessive adjectives change according to the meaning. For example, "Philip said, 'I'm having my hair cut.'" becomes "Philip said (that) he was having his hair cut."
(2. Изменение местоимений и притяжательных прилагательных: Личные местоимения и притяжательные прилагательные меняются в соответствии со смыслом. Например, "Филип сказал: 'Я стригу свои волосы.'" становится "Филип сказал, что он стрижет свои волосы.")
3. Time and Place Expression Changes: Certain words and time expressions change. For example: now → then, today → that day, tomorrow → the next/following day, here → there, come → go.
(3. Изменение выражений времени и места: Некоторые слова и выражения времени меняются. Например: now (сейчас) → then (тогда), today (сегодня) → that day (в тот день), tomorrow (завтра) → the next/following day (на следующий день), here (здесь) → there (там), come (приходить) → go (идти).)
4. Reporting Questions: The word order becomes affirmative (subject before the verb). For questions starting with a question word (what, when, etc.), the same word is used. For yes/no questions, if or whether is used. For example, "He asked me, 'Are there any oranges left?'" becomes "He asked me if/whether there were any oranges left."
(4. Перевод вопросов в косвенную речь: Порядок слов становится утвердительным (подлежащее перед сказуемым). Для вопросов, начинающихся с вопросительного слова (what, when и т.д.), используется то же самое слово. Для общих (да/нет) вопросов используется if или whether. Например, "Он спросил меня: 'Остались апельсины?'" становится "Он спросил меня, остались ли апельсины.")
Другие задания:
Помогло решение? Оставьте отзыв в комментариях ниже.
Присоединяйтесь к Телеграм-группе @top_gdz
ПрисоединитьсяМы подготовили для вас ответ c подробным объяснением домашего задания по английскому языку за 10 класс, для упражнения Reportes Statements расположенного на странице 165 к Учебник (Student's book) серии звёздный английский , starlight (старлайт) 2019 года издания для учащихся школ и гимназий.
Теперь на нашем сайте ГДЗ.ТОП вы всегда легко и бесплатно найдёте условие с правильным ответом на вопрос «Как решить ДЗ» и «Как сделать» задание по английскому языку к упражнению Reportes Statements (с. 165), авторов: Баранова (Ксения Михайловна), Дули (Дженни ), Копылова (Виктория Викторовна), Мильруд (Радислав Петрович), Эванс (Вирджиния ), ФГОС (старый) углублённый уровень обучения учебного пособия издательства Просвещение, Express Publishing.



















