Reported Orders, страница 166 - гдз по английскому языку 10 класс (starlight) учебник Баранова, Дули

Авторы: Баранова К. М., Дули Д., Копылова В. В., Мильруд Р. П., Эванс В.
Тип: Student's book (Учебник)
Серия: starlight (звёздный английский)
Издательство: Просвещение, Express Publishing
Год издания: 2019 - 2026
Уровень обучения: углублённый
Цвет обложки: белый, бирюзовый
ISBN: 978-5-09-112205-3
Допущено Министерством просвещения Российской Федерации
Популярные ГДЗ в 10 классе
Grammar Practice Section. Module 2 - страница 166.
Reported Orders (с. 166)
Условие. Reported Orders (с. 166)
скриншот условия
Reported Orders
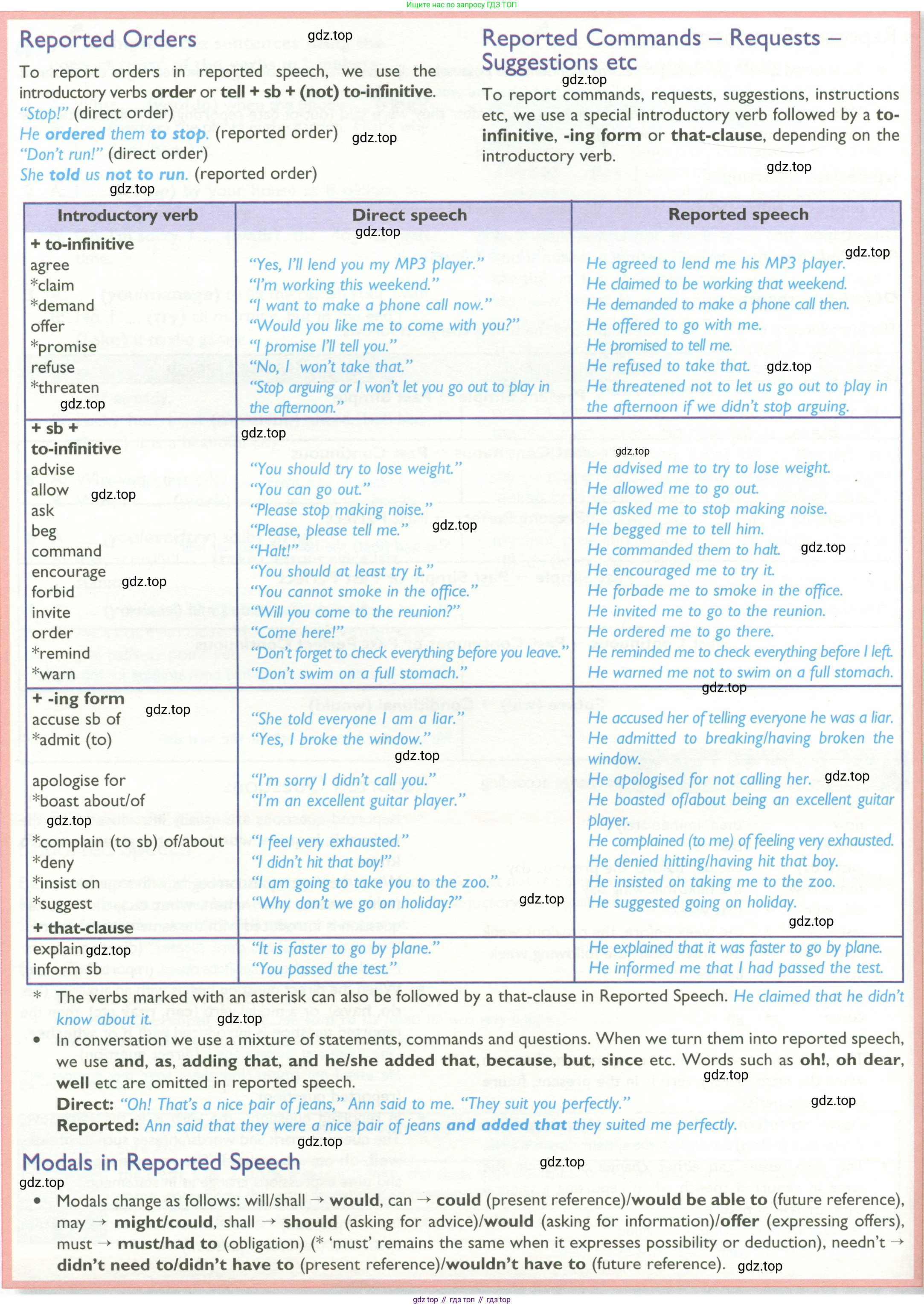
To report orders in reported speech, we use the introductory verbs order or tell + sb + (not) to-infinitive.
“Stop!” (direct order)
He ordered them to stop. (reported order)
“Don’t run!” (direct order)
She told us not to run. (reported order)
Reported Commands – Requests – Suggestions etc
To report commands, requests, suggestions, instructions etc, we use a special introductory verb followed by a to-infinitive, an -ing form or that-clause, depending on the introductory verb.
| Introductory verb | Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|---|
| + to-infinitive | ||
| agree | “Yes, I’ll lend you my MP3 player.” | He agreed to lend me his MP3 player. |
| *claim | “I’m working this weekend.” | He claimed to be working that weekend. |
| *demand | “I want to make a phone call now.” | He demanded to make a phone call then. |
| offer | “Would you like me to come with you?” | He offered to go with me. |
| *promise | “I promise I’ll tell you.” | He promised to tell me. |
| refuse | “No, I won’t take that.” | He refused to take that. |
| *threaten | “Stop arguing or I won’t let you go out to play in the afternoon.” | He threatened not to let us go out to play in the afternoon if we didn’t stop arguing. |
| + sb + to-infinitive | ||
| advise | “You should try to lose weight.” | He advised me to try to lose weight. |
| allow | “You can go out.” | He allowed me to go out. |
| ask | “Please stop making noise.” | He asked me to stop making noise. |
| beg | “Please, please tell me.” | He begged me to tell him. |
| command | “Halt!” | He commanded them to halt. |
| encourage | “You should at least try it.” | He encouraged me to try it. |
| forbid | “You cannot smoke in the office.” | He forbade me to smoke in the office. |
| invite | “Will you come to the reunion?” | He invited me to go to the reunion. |
| order | “Come here!” | He ordered me to go there. |
| *remind | “Don’t forget to check everything before you leave.” | He reminded me to check everything before I left. |
| *warn | “Don’t swim on a full stomach.” | He warned me not to swim on a full stomach. |
| + -ing form | ||
| accuse sb of | “She told everyone I am a liar.” | He accused her of telling everyone he was a liar. |
| *admit (to) | “Yes, I broke the window.” | He admitted to breaking/having broken the window. |
| apologise for | “I’m sorry I didn’t call you.” | He apologised for not calling her. |
| *boast about/of | “I’m an excellent guitar player.” | He boasted of/about being an excellent guitar player. |
| *complain (to sb) of/about | “I feel very exhausted.” | He complained (to me) of feeling very exhausted. |
| *deny | “I didn’t hit that boy!” | He denied hitting/having hit that boy. |
| *insist on | “I am going to take you to the zoo.” | He insisted on taking me to the zoo. |
| *suggest | “Why don’t we go on holiday?” | He suggested going on holiday. |
| + that-clause | ||
| explain | “It is faster to go by plane.” | He explained that it was faster to go by plane. |
| inform sb | “You passed the test.” | He informed me that I had passed the test. |
* The verbs marked with an asterisk can also be followed by a that-clause in Reported Speech. He claimed that he didn’t know about it.
• In conversation we use a mixture of statements, commands and questions. When we turn them into reported speech, we use and, as, adding that, and he/she added that, because, but, since etc. Words such as oh!, oh dear, well etc are omitted in reported speech.
Direct: “Oh! That’s a nice pair of jeans,” Ann said to me. “They suit you perfectly.”
Reported: Ann said that they were a nice pair of jeans and added that they suited me perfectly.
Modals in Reported Speech
• Modals change as follows: will/shall → would, can → could (present reference)/would be able to (future reference), may → might/could, shall → should (asking for advice)/would (asking for information)/offer (expressing offers), must → must/had to (obligation) (* 'must' remains the same when it expresses possibility or deduction), needn’t → didn’t need to/didn’t have to (present reference)/wouldn’t have to (future reference).
Решение 1. Reported Orders (с. 166)




Решение 3. Reported Orders (с. 166)
Как передавать приказы, команды, просьбы и предложения в косвенной речи, и как изменяются модальные глаголы?
Ответ:
To report orders, requests, suggestions, and commands, special introductory verbs are used, followed by a to-infinitive, an -ing form, or a that-clause. Modal verbs also change.
(Для передачи приказов, просьб, предложений и команд используются специальные вводные глаголы, за которыми следует инфинитив с частицей to, форма с окончанием -ing или придаточное предложение с that. Модальные глаголы также изменяются.)
1. Reported Orders (Приказы в косвенной речи)
Use the structure: order / tell + sb + (not) to-infinitive.
(Используйте структуру: order / tell + кто-либо + (не) инфинитив с частицей to.)
Example: "Don't run!" → She told us not to run.
(Пример: "Не беги!" → Она сказала нам не бежать.)
2. Introductory Verbs with Different Structures (Вводные глаголы с различными структурами)
| Structure (Структура) | Verbs (Глаголы) |
|---|---|
| + to-infinitive | agree, claim, demand, offer, promise, refuse, threaten (соглашаться, утверждать, требовать, предлагать, обещать, отказывать, угрожать) |
| + sb + to-infinitive | advise, allow, ask, beg, command, encourage, forbid, invite, order, remind, warn (советовать, позволять, просить, умолять, приказывать, поощрять, запрещать, приглашать, приказывать, напоминать, предупреждать) |
| + -ing form | accuse sb of, admit (to), apologise for, boast about/of, complain of/about, deny, insist on, suggest (обвинять кого-либо в, признавать, извиняться за, хвастаться, жаловаться на, отрицать, настаивать на, предлагать) |
| + that-clause | explain, inform sb (объяснять, информировать кого-либо) |
3. Modals in Reported Speech (Модальные глаголы в косвенной речи)
Modal verbs change as follows:
(Модальные глаголы изменяются следующим образом:)
will/shall → would
can → could (present reference) / would be able to (future reference)
(can → could (относится к настоящему) / would be able to (относится к будущему))
may → might/could
shall → should (asking for advice) / would (asking for information/offer)
(shall → should (просьба о совете) / would (запрос информации/предложение))
must → must/had to (obligation)
(must → must/had to (обязательство))
needn't → didn't need to/didn't have to (present reference) / wouldn't have to (future reference)
(needn't → didn't need to/didn't have to (относится к настоящему) / wouldn't have to (относится к будущему))
Другие задания:
Помогло решение? Оставьте отзыв в комментариях ниже.
Присоединяйтесь к Телеграм-группе @top_gdz
ПрисоединитьсяМы подготовили для вас ответ c подробным объяснением домашего задания по английскому языку за 10 класс, для упражнения Reported Orders расположенного на странице 166 к Учебник (Student's book) серии звёздный английский , starlight (старлайт) 2019 года издания для учащихся школ и гимназий.
Теперь на нашем сайте ГДЗ.ТОП вы всегда легко и бесплатно найдёте условие с правильным ответом на вопрос «Как решить ДЗ» и «Как сделать» задание по английскому языку к упражнению Reported Orders (с. 166), авторов: Баранова (Ксения Михайловна), Дули (Дженни ), Копылова (Виктория Викторовна), Мильруд (Радислав Петрович), Эванс (Вирджиния ), ФГОС (старый) углублённый уровень обучения учебного пособия издательства Просвещение, Express Publishing.


















